Depreciation as per companies act 2013 measures the wearing out or loss of value of a depreciable asset from use or obsolescence. Depreciation on assets can be claimed as an expense in the Profit and Loss A/c of a business.
Depreciation as per Companies Act, 2013 is applicable for assets purchased on or after 1st April 2014. It only prescribes the useful life of different assets and does not provide any specific depreciation rates.
You can use the depreciation formula and the useful life given in Schedule II of Companies Act, 2013 to calculate the rate of depreciation as per companies act. Besides, we have calculated and given the mca depreciation rates under Depreciation Rates as per companies act 2013 for AY 2023-24.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of depreciation as per Companies Act 2013, unraveling its significance and implications.
Table of Contents
Depreciation Meaning
Depreciation measures the wearing out or loss of value of a depreciable asset from use or obsolescence.
Key Points
| -Depreciation as per Companies Act 2013 applies to assets purchased on or after 1st April 2014 |
| -Depreciation formula considers the cost of the asset, the useful life of the asset and residual value. |
| – A company calculates the depreciation amount annually until the end of the useful life of an asset. |
| -Residual value is considered at a maximum of 5% of the cost of the asset. |
| -Use either SLM or WDV method of finding depreciation as per companies act. |
| -Schedule 2 of the Companies Act 2013 provides useful life of assets tangible in nature. |
| -Refer to the Chart for Depreciation Rate as per Companies Act For AY 2023-24 to calculate depreciation. |
| -To calculate depreciation on intangible assets, the provisions of AS 26 shall apply. |
| -A company charges depreciation to the Profit and Loss account. |
| – You may use the depreciation calculator to calculate the depreciation amount. |
Why is Depreciation Charged?
Depreciation as per Companies Act, 2013 treats depreciation as an expense and is shown as an expense in the Profit and Loss A/c of the company. This ensures that the financial statements are accurate.
A company claims Depreciation under the Income Tax Act, 1961 to reduce the taxable income of the company.
The difference between Depreciation as per Companies Act and Depreciation as per Income Tax Act is treated as Deferred Tax Liability and Deferred Tax Asset in the books of the company.
Depreciation as per Companies Act 2013 Calculator
Default: 5%
How to use the Depreciation Calculator?
We will understand with the help of an example.
Example: Suppose ABC Pvt Ltd purchased a Computer costing Rs 50,000 on 1st April 2021. On 31st March 2022, he wants to calculate the depreciation amount for FY 2021-22.
Residual/ Salvage value% is considered at 5%. As per the depreciation chart, the life of computers is 3 years.
Step 1: Enter the Date of Purchase of Asset as 01/04/2021 (dd/mm/yyyy)
Step 2: Enter the Cost of Asset as 50000
Step 3: Enter the Salvage/ Residual value as 5.
Step 4: Enter the Useful life of asset as 3.
Step 5: Select the Depreciation Method from the drop-down- WDV method or SLM method.
Step 6: Click on Calculate.
A depreciation chart will generate.
Click Refresh/ press F5 for a fresh calculation.
Important notes while using the calculator:
(1) Date of Purchase of Asset
Enter date in the format dd/mm/yyyy. The calculator does not support other date formats.
(2) Cost of Asset
Enter the cost of asset excluding the GST portion if you have claimed the input tax credit on the asset.
Enter the cost of asset including the GST portion if you have not claimed the input tax credit on the asset.
(3) Residual value
Residual value% is usually 5%. In calculator enter only 5. If the residual value is different for your company, enter only the number without percentage(%) sign.
(4) Useful Life of asset
Refer to the Depreciation Chart as per companies act, 2013 given in this article for the asset that you have purchased.
(5) Selecting the Depreciation method.
SLM- If you select SLM, the Depreciation amount is calculated as per SLM formula and chart is generated.
WDV- If you select WDV, the Depreciation amount is calculated as per WDV formula and chart is generated.
Depreciation Rate as per Companies Act For AY 2023-24
Schedule 2 of the Companies Act 2013 only provides useful life of assets tangible in nature. Therefore, we calculated the depreciation rates under the WDV and the SLM methods using the depreciation formula.
Below is the depreciation as per Companies act 2013 / Depreciation Chart as per Companies Act:
I. Buildings [NESD]
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| (in years) | WDV rate | SLM rate | |
| Buildings (other than factory buildings) RCC Frame Structure | 60 years | 4.87 % | 1.67 % |
| Buildings (other than factory buildings) other than RCC Frame Structure | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Factory buildings | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Fences, wells, tube wells | 5 years | 45.07 % | 19.00 % |
| Others (including temporary structure, etc.) | 3 years | 63.16 % | 31.67 % |
II. Bridges, culverts, bunders, etc. [NESD]
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Bridges, culverts, bunders, etc. [NESD] | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
III. Roads [NESD]
| Nature of assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Carpeted Roads-RCC | 10 years | 25.88 % | 9.50 % |
| Carpeted Roads-other than RCC | 5 years | 45.07 % | 19.00 % |
| Non-carpeted roads | 3 years | 63.16 % | 31.67 % |
IV. Plant and Machinery
(i) General rate applicable to plant and machinery not covered under special plant and machinery
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Plant and machinery other than continuous process plant not covered under specific industries | 15 years | 18.10 % | 6.33 % |
| continuous process plant for which no special rate has been prescribed under (ii) below [NESD] | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
| Non-carpeted roads | 3 years | 63.16 % | 31.67 % |
(ii) Special Plant and Machinery
(a) Plant and Machinery related to production and exhibition of Motion Picture Films
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Cinematograph films—Machinery used in the production and exhibition of cinematograph films, recording and reproducing equipments, developing machines, printing machines, editing machines, synchronisers and studio lights except bulbs | 13 years | 20.58 % | 7.31 % |
| Projecting equipment for exhibition of films | 13 years | 20.58 % | 7.31 % |
(b) Plant and Machinery used in glass manufacturing
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Plant and machinery except for direct fire glass melting furnaces Recuperative and regenerative glass melting furnaces | 13 years | 20.58 % | 7.31 % |
| Plant and machinery except for direct fire glass melting furnaces Moulds [NESD] | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
| Float Glass Melting Furnaces [NESD] | 10 years | 25.88 % | 9.50 % |
(c) Plant and Machinery used in mines and quarries
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Portable underground machinery and earth moving machinery used in open cast mining [NESD] | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
(d) Plant and Machinery used in Telecommunications [NESD]
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Towers | 18 years | 15.33 % | 5.28 % |
| Telecom transceivers, switching centres, transmission and other network equipment | 13 years | 20.58 % | 7.31 % |
| Telecom—Ducts, Cables and optical fibre | 18 years | 15.33 % | 5.28 % |
| Satellites | 18 years | 15.33 % | 5.28 % |
(e) Plant and Machinery used in exploration, production and refining oil and gas [NESD]
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Refineries | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
| Oil and gas assets (including wells), processing plant and facilities | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
| Petrochemical Plant | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
| Storage tanks and related equipment | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
| Pipelines | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Drilling Rig | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Field operations (above ground) Portable boilers, drilling tools, well-head tanks, etc. | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
| Loggers | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
(f ) Plant and Machinery used in generation, transmission and distribution of power [NESD]
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Thermal/ Gas/ Combined Cycle Power Generation Plant | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Hydro Power Generation Plant | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Nuclear Power Generation Plant | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Transmission lines, cables and other network assets | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Wind Power Generation Plant | 22 years | 12.73 % | 4.32 % |
| Electric Distribution Plant | 35 years | 8.20 % | 2.71 % |
| Gas Storage and Distribution Plant | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Water Distribution Plant including pipelines | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
(g) Plant and Machinery used in manufacture of steel
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Sinter Plant | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Blast Furnace | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Coke ovens | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Rolling mill in steel plant | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Basic oxygen Furnace Converter | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
(h) Plant and Machinery used in manufacture of non-ferrous metals
| Nature of assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Metal pot line [NESD] | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Bauxite crushing and grinding section [NESD] | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Digester Section [NESD] | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Turbine [NESD] | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Equipments for Calcination [NESD] | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Copper Smelter [NESD] | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Roll Grinder | 40 years | 7.22 % | 2.38 % |
| Soaking Pit | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Annealing Furnace | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Rolling Mills | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Equipments for Scalping, Slitting , etc. [NESD] | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Surface Miner, Ripper Dozer, etc., used in mines | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
| Copper refining plant [NESD] | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
(i) Plant and Machinery used in medical and surgical operations [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Electrical Machinery, X-ray and electrotherapeutic apparatus and accessories thereto, medical, diagnostic equipments, namely, Cat-scan, Ultrasound Machines, ECG Monitors, etc. | 13 years | 20.58 % | 7.31 % |
| Other Equipments | 15 years | 20.58 % | 7.31 % |
(j) Plant and Machinery used in manufacture of pharmaceuticals and chemicals [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful life as per companies act | Depreciation rate | |
WDV | SLM | ||
| Reactors | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Distillation Columns | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Drying equipments / Centrifuges and Decanters | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Vessel/storage tanks | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
(k) Plant and Machinery used in civil construction
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Concreting, Crushing, Piling Equipments and Road Making Equipments | 12 years | 22.09 % | 7.92 % |
| Heavy Lift Equipments— Cranes with capacity of more than 100 tons | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Heavy Lift Equipments— Cranes with capacity of less than 100 tons | 15 years | 18.10 % | 6.33 % |
| Transmission line, Tunneling Equipments [NESD] | 10 years | 25.88 % | 9.50 % |
| Earth-moving equipments | 9 years | 28.31 % | 10.56 % |
| Others including Material Handling /Pipeline/Welding Equipments [NESD] | 12 years | 22.09 % | 7.92 % |
(l) Plant and Machinery used in salt works [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Plant and machinery used in salt works [NESD] | 15 years | 18.10 % | 6.33 % |
V. Furniture and fittings [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| General furniture and fittings | 10 years | 25.88 % | 9.50 % |
| Furniture and fittings used in hotels, restaurants and boarding houses, schools, colleges and other educational institutions, libraries; welfare centres; meeting halls, cinema houses; theatres and circuses; and furniture and fittings let out on hire for use on the occasion of marriages and similar functions. | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
VI. Motor Vehicles [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Motor cycles, scooters and other mopeds | 10 years | 25.88 % | 9.50 % |
| Furniture and fittings used in hotels, restaurants and boarding houses, schools, colleges and other educational institutions, libraries; welfare centres; meeting halls, cinema houses; theatres and circuses; and furniture and fittings let out on hire for use on the occasion of marriages and similar functions. | 6 years | 39.30 % | 15.83 % |
| Motor buses, motor lorries, motor cars and motor taxies used in a business of running them on hire | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
| Motor buses, motor lorries and motor cars other than those used in a business of running them on hire | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
| Motor tractors, harvesting combines and heavy vehicles | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
| Electrically operated vehicles including battery powered or fuel cell powered vehicles | 8 years | 31.23 % | 11.88 % |
VII. Ships [NESD]
1. Ocean-going ships
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Bulk Carriers and liner vessels | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
| Crude tankers, product carriers and easy chemical carriers with or without conventional tank coatings. | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Chemicals and Acid Carriers: With Stainless steel tanks | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
| Chemicals and Acid Carriers: With other tanks | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Liquified gas carriers | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Conventional large passenger vessels which are used for cruise purpose also | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Coastal service ships of all categories | 30 years | 9.50 % | 3.17 % |
| Offshore supply and support vessels | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Catamarans and other high speed passenger for ships or boats | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
| Drill ships | 25 years | 11.29 % | 3.80 % |
| Hovercrafts | 15 years | 18.10 % | 6.33 % |
| Fishing vessels with wooden hull | 10 years | 25.88 % | 9.50 % |
| Dredgers, tugs, barges, survey launches and other similar ships used mainly for dredging purposes | 14 years | 19.26 % | 6.79 % |
2. Vessels ordinarily operating on inland waters—
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Speed boats | 13 years | 20.58 % | 7.31 % |
| Other vessels | 28 years | 10.15 % | 3.39 % |
VIII. Aircrafts or Helicopters [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Aircrafts or Helicopters [NESD] | 20 years | 13.91 % | 4.75 % |
IX. Railways sidings, locomotives, rolling stocks, tramways and railways used by concerns, excluding railway concerns [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Railways sidings, locomotives, rolling stocks, tramways and railways used by concerns, excluding railway concerns [NESD] | 15 years | 18.10 % | 6.33 % |
X. Ropeway structures [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Ropeway structures [NESD] | 15 years | 18.10 % | 6.33 % |
XI. Office equipment [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Office equipment [NESD] | 5 years | 45.07 % | 19.00 % |
XII. Computers and data processing units [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Servers and networks | 6 years | 39.30 % | 15.83 % |
| End user devices, such as, desktops, laptops, etc. | 3 years | 63.16 % | 31.67 % |
XIII. Laboratory equipment [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| General laboratory equipment | 10 years | 25.88 % | 9.50 % |
| Laboratory equipments used in educational institutions | 5 years | 45.07 % | 19.00 % |
XIV. Electrical Installations and Equipment [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Electrical Installations and Equipment [NESD] | 10 years | 25.88 % | 9.50 % |
XV. Hydraulic works, pipelines and sluices [NESD]
| Nature of Assets | Useful Life | Depreciation rate | |
| WDV | SLM | ||
| Hydraulic works, pipelines and sluices [NESD] | 15 years | 18.10 % | 6.33 % |
Download Depreciation as per Companies Act 2013 pdf
Important points to remember while calculating depreciation as per companies act, 2013 on tangible assets
1.Depreciation on a pro-rata basis is calculated from the date of such addition or sale or destruction in the following scenarios
(i) Any addition is made to any asset.
(ii) Any asset is sold
(iii) Any asset is discarded, demolished or destroyed.
2.The calculations of the extra depreciation for double shift working and for triple shift working must be made separately in the proportion which the number of days for which the concern worked a double shift or triple shift bears to the normal number of working days during the year.
For this purpose, the typical number of working days during the year shall be deemed to be –
(a) A seasonal factory or concern- The number of days on which the factory or concern actually worked during the year or 180 days, whichever is greater ;
(b) Others- The number of days on which the factory or concern actually worked during the year or 240 days, whichever is greater.
3.Double Shift depreciation- Depreciation increases by 50% for the period in which the asset is in use for double shift.
4.Triple Shift depreciation- Depreciation increases by 100% for the period in which the asset is in use for triple shift.
5.NESD means No extra shift depreciation. Schedule II has certain assets with NESD. A business cannot charge extra shift depreciation in respect of such assets.
6. Residual value of an asset must not be more than 5% of the asset’s original cost.
7. Depreciation rate as per Schedule II of Companies Act, 2013 applies to assets purchased on or after 1st April 2014.
Also read depreciation as per Companies Act, 1956.
Business can opt any of the below methods of depreciation calculation as per companies act.
(1)Straight Line Method (SLM)
It is one of the simplest methods of calculating depreciation as per companies act. Under this method, the total depreciable amount is allocated evenly every year over the asset’s useful life.
(2) Written Down Value Method (WDV)
It is also known as the reducing balance method or declining balance method of calculating depreciation as per companies act. Under this method, we charge the depreciation rate on the reducing balance of the asset.
For example, in the 1st year, the depreciation rate is calculated on the asset’s book value at the end of the financial year. Then, in the 2nd year, the depreciation amount of the 1st year is reduced from the initial book value of the asset to arrive at a new reduced or written down book value on which we calculate the depreciation. We will continue this process until the asset is reduced to its residual value at the end of the asset’s life.
How to calculate depreciation as per Companies Act 2013 using WDV method
You can use the below Depreciation formula to calculate the depreciation rate.
Depreciation WDV Formula
Annual Depreciation Rate= {1-(Scrap value of asset/Cost of asset)^(1/remaining useful life of asset)} x 100
Pro-rata depreciation Rate= {1-(Scrap value of asset/Cost of asset)^(1/remaining useful life of asset)} x [Number of days from date of asset purchased till financial year-end/365] x 100
The symbol ^ known as Caret represents an exponent. For instance, 2^3 is same as 23
Likewise, in the above formula ^ is used as an exponent.
Use a standard keyboard, scientific calculator or calculator on your mobile to calculate easily using this formula. The feature ^ is not available in a simple calculator so it becomes tedious to calculate using a simple calculator.
Cost of Asset: To calculate depreciation on a capital asset, you must consider the asset’s cost, excluding the GST amount if you are claiming input tax credit (ITC) on that asset.
If you want to consider the total asset amount including GST for calculating depreciation as per companies act, then you should not claim ITC on that asset.
As per Sec 2(19) of CGST Act, Where the registered person has claimed depreciation on the tax component of the cost of capital goods and plant and machinery under the provisions of the Income-tax Act, 1961, the input tax credit on the said tax component shall not be allowed.
We shall understand how to calculate depreciation as per companies act with example as below
Examples to calculate Depreciation as per companies act using WDV method
Example 1: Asset Purchased after 1st April 2014.
Suppose ABC Ltd purchased a laptop on 1st April 2019 for R s 10,000.
We shall calculate the rate of depreciation using the above depreciation formula
Step 1: Finding the Scrap value of asset
As per companies act, the residual value of an asset should not be more than 5% of the asset’s original cost.
So, the Scrap value of asset= Cost of Asset x 5%
=10000 X 5%
Scrap value= Rs 500
Step 2: Finding Remaining useful life of an asset
Asset purchased is laptop. The useful life of laptop given under schedule II of Companies Act 2013 is 3 years.
Useful life of asset= 3 years
Step 3: Finding Depreciation rate
Substituting the values in the depreciation formula we get
Depreciation rate= {1-(500/10000)^(1/3)} X 100
=0.63159 x 100
=63.16%
Depreciation rate for laptop is 63.16%
Now, that we know the depreciation rate we can calculate the depreciation amount during the useful life of the asset (laptop)
Step 4: Depreciation schedule as per Companies Act during the useful life of asset (laptop)
| Year | Opening WDV | Depreciation | Closing WDV |
| 1 | 10000 | 10000 X 63.16% = 6316 | 10000-6316 =3684 |
| 2 | 3684 | 3684 X 63.16% =2326.81 | 3684-2326.81 =1357.19 |
| 3 | 1357.19 | 1357.19 X 63.16% =857.20 | 1357.19-857.20 =500 |
Example 2: Asset Purchased before 1st April 2014.
Suppose XYZ Ltd purchased a building on 1st April 2000 for Rs 100,000. The company was charging depreciation on the Straight-line method @ 1.63% as per the rate of depreciation prescribed in the Companies Act, 1956.
Step 1:Transition effect of depreciation
Calculate the amount of depreciation charged till FY 2013-14
Depreciation amount= Asset Value X Depreciation Rate X Number of years
Substituting the values, we get
=100000 X 1.63% X 4
Depreciation amount=Rs 6520
Step 2: Find Carrying value of the asset as of 1st April 2014
Carrying value of Asset = Original cost of asset – Accumulated Depreciation
Substituting the values, we get
Carrying value of asset on 1st April 2014= 100000 – 6520
Carrying value of asset =Rs 93480
Step 3: Find Depreciation rate as per Companies Act, 2013
From 1st April 2014, depreciation as per schedule II of Companies Act, 2013 is applicable
We use the below depreciation formula to arrive at the depreciation rate
Depreciation Rate= {1-(Scrap value of asset/Carrying value of asset)^(1/remaining useful life of asset)} x 100
Scrap value of asset= Carrying value of asset on 1st April 2014 X 5%
=93480 X 5%
Scrap value= Rs 4674
Remaining useful life of asset= 30-4 years (as per schedule II)
=26 years
Depreciation rate= {1-(4674/93480)^(1/26)} X 100
=0.10883X 100
Depreciation rate=10.88%
How to calculate depreciation as per Companies Act 2013 using SLM method
Depreciation SLM Formula
Annual Depreciation = {Cost of asset- Salvage Value of asset} / Useful life of asset
Cost of asset= Cost of asset on the date of purchase
Salvage value of asset= cost of asset x Residual value of asset. (max residual value is 5%)
The useful life of asset= Useful life of the asset as given under Schedule II of Companies Act 2013 for different asset classes.
Depreciation rate= (Annual Depreciation/ Cost of Asset)x100
You can also calculate depreciation under Straight line method using Excel formula.
SLM Formula in Excel
=SLN(Cost,Salvage value, life of asset)
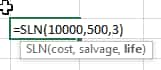
Examples to calculate Depreciation as per companies act using SLM Method
Example 1: Asset Purchased after 1st April 2014.
Suppose ABC Ltd purchased a laptop on 1st April 2019 for Rs 10,000.
We shall calculate the rate of depreciation using the above depreciation formula
Step 1: Finding the Salvage value of asset
As per the companies act, the residual value of an asset should not be more than 5% of the asset’s original cost.
So, Salvage value of asset= Cost of Asset x 5%
=10000 X 5%
Salvage value= Rs 500
Step 2: Finding Remaining useful life of asset
The asset purchased is a laptop. The useful life of a laptop given under schedule II of Companies Act 2013 is three years.
Useful life of asset= 3 years
Step 3: Finding Depreciable amount
Depreciable amount= cost of the asset – Salvage value of asset
Depreciable amount= 10000-500
=9500
Step 4: Finding Annual Depreciation amount
Substituting the values in the depreciation formula we get
Annual Depreciation = 9500/ 3
= 3166.67
Step 4: Finding Depreciation rate
Substituting the values in the SLM depreciation formula.
Depreciation rate= {3166.67/10000}X100
Depreciation rate as per SLM =31.67 %
Step 4: Depreciation schedule as per Companies Act during the useful life of asset (laptop)
| Year | Opening Book value | Depreciation | Closing Book Value |
| 1 | 10000 | 10000 X 31.67 % = 3166.67 | 10000-3166.67 =6833.33 |
| 2 | 6833.33 | 10000 X 31.67 % = 3166.67 | 6833.33-3166.67 =3167.30 |
| 3 | 3666.66 | 10000 X 31.67 % = 3166.67 | 3666.66-3166.67 =499.99~ 500 |
Recording Journal entry for Depreciation in Tallyprime
Now that you know the concept let us see how to record a Depreciation Journal entry in Tallyprime
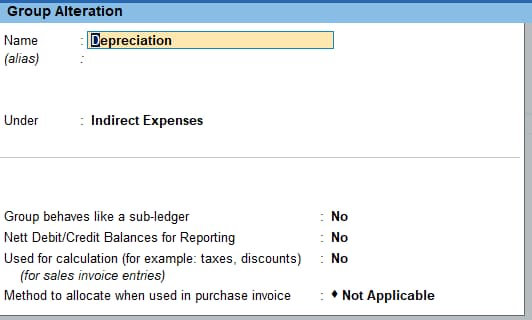
Step1: Firstly, you must create a group named “Depreciation” under the head Indirect Expenses. By doing this, when you record a journal entry for depreciation, it is automatically charged as depreciation expense in Profit and Loss A/c.
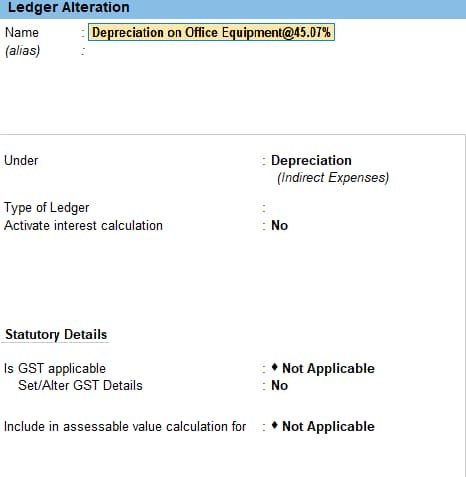
Step 2: Now, create depreciation on a specific asset ledger selecting the group as depreciation.
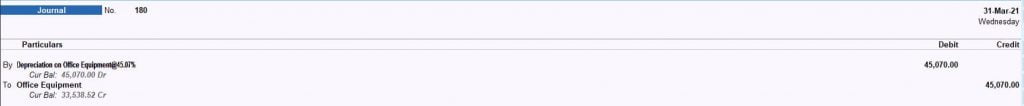
Step 3. Record journal entry in Tallyprime using voucher type “Journal Voucher” by pressing key F7
Depreciation as per companies act journal entry example
Suppose, ZYZ company purchases office equipment on 1-04-2020 @ Rs 1,00,000. Then, we must charge a WDV depreciation rate of 45.07% as per the companies act, 2013.
Depreciation amount for 1st year is 100,000 x 45.07%= Rs 45,070.
Below is the journal entry to record depreciation on office equipment.
Depreciation on computers Dr 45,070
To Office equipment 45,070
Depreciation entry in Tallyprime
Depreciation on Intangible Assets as per Companies act 2013
The Companies Act identifies the below assets as Intangible assets
a) Brand names
(b) Mastheads and publishing titles
(c) Computer software
(d) Licences and franchises
(e) Copyrights, and patents and other industrial property rights, service and operating rights
(f) Recipes, formulae, models, designs and prototypes
(g) Intangible assets under development
For calculation of depreciation on intangible assets, the provisions of accounting standard 26 (AS 26) shall apply. Furthermore, Schedule II of Companies Act, 2013 is not applicable in the case of intangible assets.
Amortisation in case of intangible assets may be done as follows
Depreciation formula for Intangible assets
Amortisation rate= (Amoritsation amount/ Cost of Intangible assets) x 100
Amortisation amount= Cost of Intangible assets x Actual Revenue for the year/ Projected revenue from Intangible asset
where,
Cost of Intangible asset (A)= cost incurred by the company under the AS 26
Actual revenue for the year= Actual revenue (Toll charges) received during the accounting year.
Projected Revenue from Intangible Asset = Total projected revenue from the Intangible Assets as provided to the project lender at the time of financial closure/agreement.
Also read about the Intangible assets depreciation on official MCA website
Difference between Depreciation as per Companies Act and Income Tax Act
| Depreciation as per Companies Act, 2013 | Depreciation as per Income Tax Act, 1961 |
| Depreciation is calculated on a pro-rata basis. | Depreciation calculation is done either full rate or half rate based on 180 days criteria. |
| Pro-rata basis-It is calculated from the date of purchase of the asset to the end of the financial year. | If the asset is in use for more than 180 days, one can claim the full depreciation rate. And if the assets are in use for less than 180 days, one can claim half the depreciation rate. |
Depreciation as per Companies Act FAQs
(1)What is a Depreciable amount?
It is the cost of an asset less its residual value.
(2)What is useful life as per companies act?
Useful life of an asset is either
(a) the period of time over which an asset is expected to be used by the enterprise or
(b)the number of production or similar units expected to be obtained from the asset by the enterprise.
(3)What is Residual Value?
It is the amount an organisation expects to obtain for an asset at the end of its useful life after deducting the expected costs of disposal. As per the Companies Act, a maximum of 5% of the asset is allowable as residual value.
(4)What is carrying amount?
It is the amount at which we recognise an asset in the balance sheet, net of any accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses thereon.
(5) Is it mandatory to charge depreciation as per Companies Act?
As per accounting standard 6 (AS 6), it is mandatory to claim depreciation as per companies act because it has a significant effect in determining and presenting a company’s financial position and results. In addition to this, charging depreciation becomes mandatory if the company desires to declare a dividend or pay managerial remuneration.
(6)What is depreciation on plant and machinery as per companies act?
Depreciation on plant and machinery as per companies act 2013 is 18.10% under WDV & 6.33% under SLM. For depreciation rates on Special plant and machinery, refer the Schedule II given above.
(7)What is depreciation on mobile as per companies act 2013?
The treatment of mobile is the same as plant and machinery. Therefore, depreciation on mobile is 18.10% under WDV & 6.33% under SLM. Also, the mobile phone useful life as per companies act is 15 years.
(8)What is Depreciation on software as per companies act?
The treatment of software is the same as computers. Therefore, the software depreciation rate as per Companies act is 63.16% under WDV & 31.67% under SLM.
(9) How much depreciation can I claim on my car?
The treatment of car is the same as Motor cars under Motor vehicles. Therefore, depreciation on the car as per companies act 2013 is 31.23% under WDV & 11.88% under SLM.
(10)Can we claim ITC on capital goods under GST?
If you claim depreciation on assets purchased, including the GST amount, you cannot claim ITC. If you claim Input Tax Credit (ITC), then you cannot claim depreciation on the tax amount. You can either claim depreciation or ITC on the tax portion of the asset.
(11)What is the Deferred Asset or Deferred Liability?
The difference in the amount of depreciation as per companies act and income tax act results in Deferred Asset or Deferred Liability. Deferred Asset or Deferred Liability is shown in the balance sheet of the company.
(12)What is Depreciation on laptop as per Companies act?
Depreciation on laptop as per companies act 2013 is 63.16% under WDV & 31.67% under SLM.
(13) What is the depreciation rate on tally software ?
The treatment of tally Software is the same as computers. Therefore, the Depreciation rate on tally software as per companies act 2013 is 63.16% under WDV & 31.67% under SLM.
(14)What is Depreciation on Computers as per companies act?
Depreciation on computers as per companies act 2013 is 63.16% under WDV & 31.67% under SLM.
(15)What is Depreciation on Office Equipment?
Office Equipment depreciation rate is 45.07% under WDV and 19% under SLM.
(16)What is Depreciation on Furniture?
Depreciation on furniture as per companies act 2013 is 25.88% under WDV & 9.50% under SLM. And Life of Furniture, as per the companies act 2013, is ten years.
(17)What is Depreciation on Building?
The depreciation rate for building as per companies act 2013 is 4.87% under WDV & 1.67% under SLM. For depreciation for a specific type of building, see the above depreciation chart as per companies act.
(18)What is Depreciation on Motor car?
Motor car depreciation rate as per companies act is 31.23% under WDV & 11.88% under SLM.
(19)What is the useful life of software as per Companies Act 2013?
The useful life of software as per Companies Act 2013 is 3 years. You may refer to the depreciation rate chart for useful life of other assets.
(20) What is the depreciation rate on inverter battery as per companies act?
The inverter battery is treated as Plant and Machinery. Therefore, the depreciation rate on inverter battery is 18.10% under WDV & 6.33% under SLM as per Companies Act.
(21)What is the vehicle depreciation rate as per companies act?
Please refer the schedule for Motor Vehicles [NESD] to get the accurate vehicle depreciation rate as per companies act.
Depreciation is one of the critical aspects of business and adhering to the regulations prescribed by the Depreciation as per Companies Act, 2013, businesses can ensure accurate financial statements. In this article, we have shed light on the significance of depreciation, methods of depreciation allowed under the Act, and Depreciation calculator to calculate depreciation amount accurately.
We hope that you got a detailed overview of Depreciation as per Companies Act 2013. If you have any queries, you can post them in the comments section and we will answer as quickly as possible.
